My Morning Routine: Listening to My Heart
What’s HRV and why should I care?
I’ve written about my morning routine in previous blogs and why it’s important to my wellbeing and me. Meditation and breathing exercises are key components of that routine and so is a movement practice that sets the tone of my day. But how do I know that this routine is effective? I did quite a bit of research to find some way to quantify my day-to-day improvement since I knew that using just my “gut feeling” wasn’t enough. Having a scientific background led me to look at measuring my heart rate, blood pressure and sleep cycles and I concluded that the best measurement of effectiveness was to look at Heart Rate Variability (HRV).
I first heard of HRV while listening to Ben Greenfield’s fitness podcast. He spoke about it often and wrote about it in his book, Beyond Training. He even has his own app to use for an iPhone. Unfortunately, I’m more of a Android guy and needed to look elsewhere. After an extensive search and multiple trials, I found one that I’ve used for the past year: Elite HRV.
So what is HRV? According to Elite HRV’s website, “Basic Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is the measured changes of the time intervals between successive heart beats. Unlike Heart Rate (HR) that averages the number of heart beats per minute, HRV looks much closer at the small fluctuations of the heart that occur in response to internal and external events. “
For those of you with the propeller hats, there’s a more scientific explanation. This one is from Polar.com:
Heart rate varies with every heartbeat. Heart rate variability (HRV) is the variation of beat to beat intervals, also known as R-R intervals. Electrocardiogram (ECG) is the electric signal originating from heart. The most distinct feature of the ECG is the QRS complex, which consists of the Q, R and S waves and originates from the electrical activation of the heart ventricles. Figure 1 illustrates the variation of time between R-R intervals.

HRV indicates the fluctuations of heart rate around an average heart rate. An average heart rate of 60 beats per minute (bpm) does not mean that the interval between successive heartbeats would be exactly 1.0 sec., instead they may fluctuate/vary from 0.5 sec up to 2.0 sec.
HRV is affected by aerobic fitness. HRV of a well-conditioned heart is generally large at rest. Other factors that affect HRV are age, genetics, body position, time of day, and health status. During exercise, HRV decreases as heart rate and exercise intensity increase. HRV also decreases during periods of mental stress. HRV is regulated by the autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic activity decreases heart rate and increases HRV, whereas sympathetic activity increases heart rate and decreases HRV.
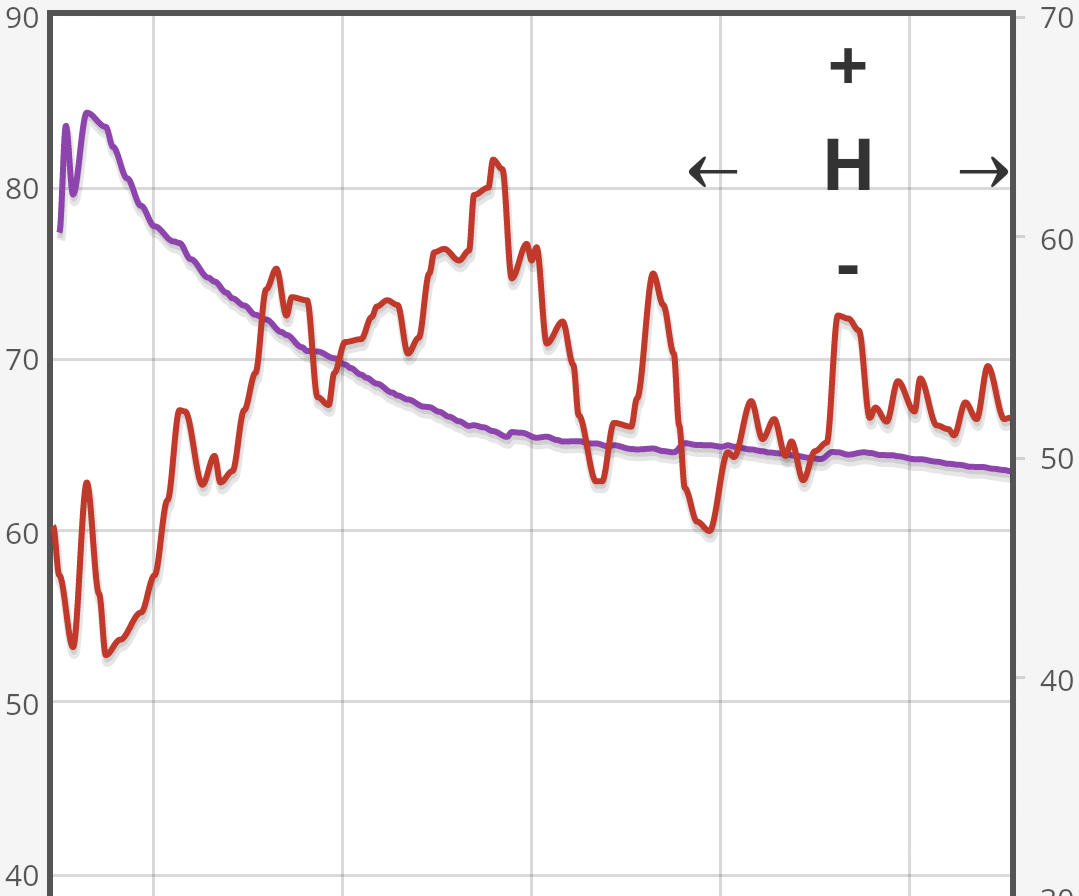
If you didn’t quite comprehend what was stated above, don’t worry. The takeaway is that HRV measures the balance of your nervous system. It lets you know if you’re more in the “fight or flight” or “rest and relaxation” mode. By measuring my HRV daily, I’m able to know if my morning routine, physical training, and sleep are being optimized.
Without fail, my readings have given me instant feedback about how my body is reacting. After hard training days, my HRV is usually lower and it gives me an idea about how I’m going to attack the day. It also gives me excellent feedback on when I’m over-reaching or over-training. It was interesting that after last month’s Spartan Race, my morning readings reflected the effects on my HRV:
[one_half]
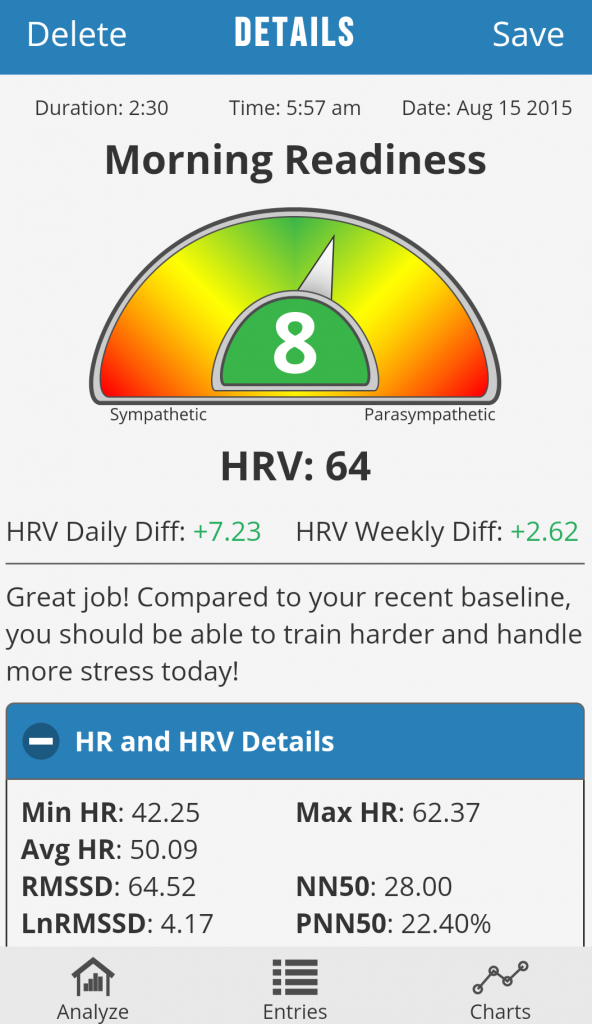
My HRV the morning of the race:
[/one_half]
[one_half_last]
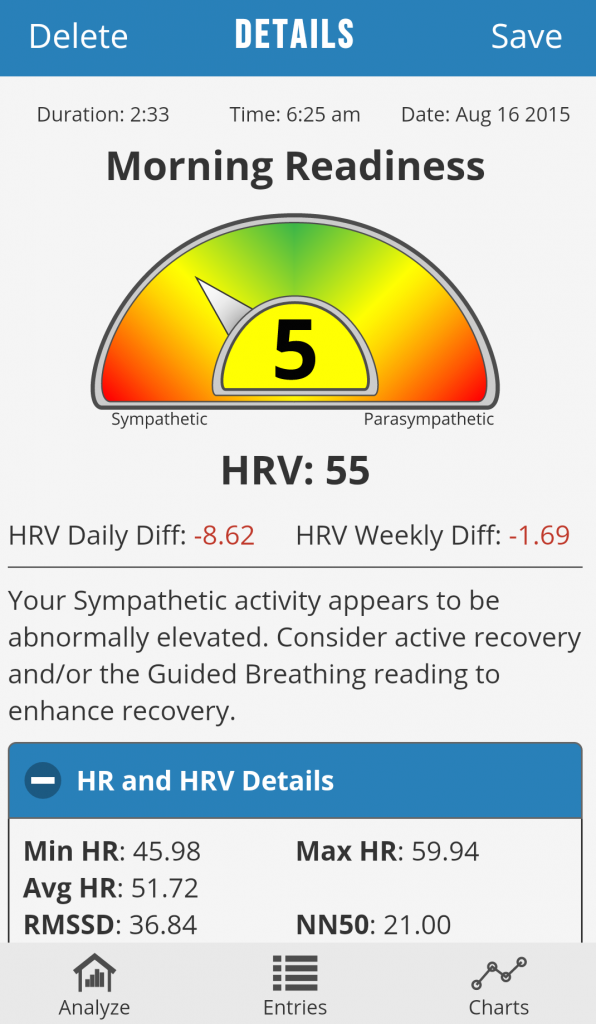
My HRV the following morning:
[/one_half_last]
Due to the information and knowledge that I’ve gained by measuring HRV, I decided to use it as a tool for treating patients. For our Work Hardening patients, we’ve collected six months of measurements to track the effectiveness of the program as well as looking for trends in patients. It’s been interesting to note that patients who’ve come in with low readings often struggle with the program and exhibit weak cardiovascular systems. I believe monitoring HRV during our patient exercise routines will become an integral part of their therapy treatment program and in the future, I hope to be involved with a medical model that is specific to patients in this capacity.
[two_third]
If you are interested in monitoring your HRV, you’ll need a heart rate monitor. I’ve tried several and so far we’ve had the best results with Polar’s H7. Also, there are several apps that are compatible with the Polar H7 (and other bluetooth HR monitors) and can be easily found on the internet. We use the Elite HRV app (compatible with Google Play and App Store devices) and you can download it here. Start by taking a reading as soon as you wake up and then several more during your exercise routine. If you have any questions regarding this topic, feel free to email me or stop by our WORC site.
[/two_third]
[one_third_last]

[/one_third_last]